Bio Septic Tank in Madurai | Manufacturer & Installation

Home About Us Products STP & ETP Plants RCC Bio Septic Tank FRP Bio Septic Tank SS Bio Digester Tank SS TRAP BOM Sump Tank Projects & Events Blog Contact X Free Consulting Bio Septic Tank in Madurai Bio Septic Tank in Madurai – Sustainable Wastewater Management With rapid urban growth in Madurai, managing sewage efficiently has become essential. Bio septic tanks provide an eco-friendly and cost-effective solution for residential, commercial, and industrial wastewater treatment. Unlike conventional septic tanks, bio septic tanks use natural bacterial digestion to break down waste and release treated water safely into the soil. Why Choose a Bio Septic Tank in Madurai? Madurai’s soil conditions and increasing water scarcity demand sustainable sewage solutions. Bio septic tanks help reduce groundwater pollution and minimize manual cleaning. RCC Bio Septic Tanks Ideal for long-term and heavy-load usage FRP Bio Septic Tanks Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and easy to install Bio Digesters Advanced anaerobic digestion systems Our Madurai Sites FRP Bio Tank Melur, Madurai RCC Bio Tank Thirupparankundram, Madurai FRP Bio Tank Anna Nagar, Madurai RCC Bio Tank Thirumangalam, Madurai Why Choose a Bio Septic Tank in Madurai? Madurai’s soil conditions and increasing water scarcity demand sustainable sewage solutions. Bio septic tanks help reduce groundwater pollution and minimize manual cleaning. Quick installation support Long-lasting materials Expert technical guidance After-sales service & maintenance Contact Nexsa Bio today Installing a bio septic tank in Madurai is a smart investment for sustainable living and environmental protection. Choose Nexsa Bio for quality, reliability, and eco-friendly wastewater treatment solutions. Contact Nexsa Bio today for the best bio septic tank price and installation in Madurai. Are you ready to take our service? We at Nexsa Bio are proud to be the best Bio septic tank manufacturer in Tamil Nadu, offering sustainable sanitation solutions for every sector. Contact Us We Post Everything That You Need to Know Useful Links Home About Us Bio Antizyme Blog Contact Us Privacy Policies About us Our Mission, A World Powered by Renewable Energy Copyright © 2025 Nexsa Bio. All Rights Reserved.
Why Bio Septic Tanks Are Mandatory for Schools, Hostels & Hospitals in India

Home About Us Products STP & ETP Plants RCC Bio Septic Tank FRP Bio Septic Tank SS Bio Digester Tank SS TRAP BOM RCC Precast Water Tank Projects & Events Blog Contact X Free Consulting Bio Septic Tanks for Schools, Hostels & Hospitals: Why They Are Now Mandatory Watch Video Introduction Schools, hostels, and hospitals generate large amounts of wastewater daily from toilets, bathrooms, kitchens, and cleaning areas. Traditional septic tanks often leak, smell, require frequent desludging, and contaminate groundwater. With rising hygiene needs, strict environmental rules, and public health requirements, bio septic tanks have become essential for modern institutions. They provide a clean, odor-free, and eco-friendly sewage treatment solution that meets today’s standards Why Bio Septic Tanks Are Becoming Mandatory for Institutions To Meet Pollution Control Board (PCB) Guidelines Educational and healthcare institutions must comply with TNPCB/CPCB norms for treated water quality.Traditional septic tanks cannot meet standards for: BOD COD TSS pH Pathogen removal However, bio septic tanks consistently meet PCB-approved discharge levels, making them the safest and most compliant solution. To Prevent Groundwater Contamination Schools and hostels are usually built in areas with: High water table Borewells for drinking water Children and staff dependent on groundwater Old-style septic tanks leak untreated sewage into the soil, causing: Contaminated drinking water Water-borne diseases Soil pollution Mosquito breeding Bio septic tanks, in contrast, are completely sealed, leak-proof, and treat sewage before releasing it into the ground or reuse systems. To Maintain a Hygiene-Safe Environment Schools and hospitals cannot afford: Foul smell Mosquito or insect breeding Overflow during rainy seasons Sewage backflow during peak usage Bio septic systems operate using anaerobic bacteria and bio-media technology that: Eliminates odor Prevents sludge accumulation Ensures smooth, continuous operation Maintains ultra-clean surroundings This is crucial for environments where children, patients, and staff must be protected from infections. To Reduce Maintenance Cost & Desludging Issues Institutions often struggle with: Frequent desludging High sewage tanker costs Operational disruptions Improper waste disposal Bio septic tanks are low-maintenance and often operate for years without desludging because: Bacteria naturally digest waste Sludge formation is minimal No chemicals or electricity needed This results in massive long-term cost savings. To Support Government & Educational Safety Mandates Key policies driving mandatory adoption: Swachh Bharat Abhiyan School Hygiene & Child Safety Norms National Education Policy (NEP 2020) Hospital Waste Management Rules Smart City & Safe City Projects All recommend or require institutions to implement eco-friendly, decentralized wastewater treatment systems — exactly what bio septic tanks provide. Ideal for Space-Limited Campuses Schools and hospitals often have restricted land space.Bio septic tanks (especially FRP models): Require minimal area Are lightweight and easy to install Can be placed even in tight or underground spaces Work without machinery or complex pipelines This makes them perfect for urban campuses and commercial buildings. Benefits of Bio Septic Tanks for Schools, Hostels & Hospitals No foul smell No sewage overflow No chemical usage No mosquito breeding No groundwater contamination PCB-approved discharge quality Very low maintenance Safe for children and patients Long lifespan (RCC & FRP options) Suitable for 10 users to 10,000 users Conclusion With increasing environmental regulations and hygiene expectations, schools, hostels, and hospitals must move away from outdated septic tanks. Bio septic tanks are now a mandatory, reliable, and future-ready solution that ensures safety, compliance, and sustainability. Nexsa Bio is proud to support institutions in building a cleaner, healthier future — one installation at a time. 💧 Safe Water. Safe Students. Safe Patients. Powered by Nexsa Bio. Our Latest Blogs 27Nov admin@gmail.com Uncategorized Why Bio Septic Tanks Are Mandatory for Schools, Hostels & Hospitals in India 04Nov admin@gmail.com Uncategorized Current Necessity of Wastewater Treatment with Bio Septic Tanks in India 27Oct admin@gmail.com Uncategorized Nexsa Bio Sewage System at Hyundai Motors Meets TNPCB Water Quality Standards We Post Everything That You Need to Know Useful Links Home About Us Bio Antizyme Blog Contact Us Privacy Policies About us Our Mission, A World Powered by Renewable Energy Copyright © 2025 Nexsa Bio. All Rights Reserved.
Current Necessity of Wastewater Treatment with Bio Septic Tanks in India

Home About Us Products STP & ETP Plants RCC Bio Septic Tank FRP Bio Septic Tank SS Bio Digester Tank SS TRAP BOM RCC Precast Water Tank Projects & Events Blog Contact X Free Consulting A Wastewater Perspective Need for Bio Septic Tanks in India Current Necessity of Wastewater Treatment with Bio Septic Tanks in India (With Statistics) Introduction Necessity of Wastewater Treatment with Bio Septic Tanks in India India is home to over 1.4 billion people — and with rapid urbanization, the country faces a serious challenge: untreated wastewater pollution. According to the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB), India generates nearly 72,368 million liters per day (MLD) of sewage, but only 28% is effectively treated. The rest contaminates rivers, lakes, and groundwater — posing major risks to health and the environment. This growing problem has made bio septic tanks a modern, sustainable necessity for wastewater treatment across residential, commercial, and industrial sectors. The Wastewater Challenge in India Key Statistics These statistics highlight a pressing need for localized, low-maintenance wastewater solutions — and that’s where bio septic tanks play a transformative role. Urban Sewage Generation India’s urban areas generate about 72,000 MLD of sewage, but existing treatment capacity is only around 20,000 MLD. Untreated Discharge A small river named Duden flows by their place and supplies it with the necessary Groundwater Contamination A small river named Duden flows by their place and supplies it with the necessary What Are Bio Septic Tanks? Bio septic tanks are eco-friendly sewage treatment systems that use natural bacteria and bio-media technology to break down organic waste into clean, odorless water. Unlike traditional septic tanks, they: Don’t require frequent desludging. Prevent groundwater pollution. Produce treated water suitable for reuse (gardening, flushing, etc.). Operate without electricity in most cases. Why Bio Septic Tanks Are the Need of the Hour 1. Environmental Protection Bio septic tanks prevent harmful effluent from entering soil and water bodies, helping protect rivers like the Ganga, Yamuna, and Cauvery from sewage pollution. 2. Cost-Effective & Low Maintenance They eliminate the need for large-scale infrastructure, desludging, or chemical treatment — saving both cost and effort for homeowners and industries. 3. Compliance with Pollution Control Board (PCB) Norms Modern bio septic systems like Nexsa Bio’s are designed to meet PCB-approved effluent standards, ensuring safe disposal or reuse. 4. Ideal for Urban and Rural Areas Urban: Can be installed in apartments, industries, and institutions where space is limited. Rural: Provides decentralized wastewater treatment where sewerage systems don’t exist. 5. Supports National Missions Swachh Bharat Abhiyan – promoting clean sanitation. Jal Jeevan Mission – ensuring safe water and wastewater reuse. Smart Cities Mission – encouraging green building infrastructure. Conclusion With only a fraction of India’s sewage being treated, bio septic tanks are no longer optional — they are essential. These systems offer a sustainable, cost-effective, and regulatory-compliant way to manage wastewater at the source. At Nexsa Bio, we are proud to lead this change through RCC and FRP bio septic solutions that help households, industries, and institutions contribute to a cleaner, greener India. 💧Clean Water. Sustainable Future. Powered by Nexsa Bio. Our Latest Blogs 26Sep admin@gmail.com Bio Septic Tanks | Uncategorized Bio Septic Tanks in India | A Revolution in Wastewater Management admin@gmail.com Uncategorized Current Necessity of Wastewater Treatment with Bio Septic Tanks in India 27Oct admin@gmail.com Uncategorized Nexsa Bio Sewage System at Hyundai Motors Meets TNPCB Water Quality Standards We Post Everything That You Need to Know Useful Links Home About Us Bio Antizyme Blog Contact Us Privacy Policies About us Our Mission, A World Powered by Renewable Energy Copyright © 2025 Nexsa Bio. All Rights Reserved.
Nexsa Bio Sewage System at Hyundai Motors Meets TNPCB Water Quality Standards

Home About Us Products STP & ETP Plants RCC Bio Septic Tank FRP Bio Septic Tank SS Bio Digester Tank SS TRAP BOM RCC Precast Water Tank Projects & Events Blog Contact X Free Consulting Nexsa Bio Sewage System at Hyundai Motors Achieves PCB-Approved Water Quality Standards Nexsa Bio’s sewage treatment system at Hyundai Motors India Pvt. Ltd., Sriperumbudur, achieves TNPCB-approved treated water quality. Learn more about the test results. Materials Made with high-grade reinforced cement concrete for durability. Installation On-site delivery and expert installation support provided across Tamil Nadu. Applications Ideal for homes, apartments, hospitals, industries, canteens, schools, and malls. Introduction In the era of industrial sustainability, Hyundai Motors India Pvt. Ltd., Sriperumbudur, has taken a major step toward eco-friendly wastewater management. Partnering with Nexsa Bio, an innovator in bio sewage and wastewater treatment technology, Hyundai implemented a bio sewage treatment system designed to meet stringent environmental standards. Recently, a water treatment test report (Ref: KSEL/AUG-3934/H/25-26, dated Sep 02, 2025) confirmed that the treated water quality from the Nexsa Bio system fully complies with the Tamil Nadu Pollution Control Board (TNPCB) norms — showcasing excellent treatment performance and environmental responsibility. About the Installation The system treats domestic wastewater generated within the facility and ensures the output is safe for discharge or reuse as per TNPCB guidelines Client Hyundai Motors India Pvt. Ltd. Location Sriperumbudur, Tamil Nadu System Type Nexsa Bio Sewage Treatment Plant Sample Collected 27.08.2025 Analysis Completed 02.09.2025 Testing Laboratory Reference KSEL/AUG-3934/H/25-26 Water Quality Test Results The treated water sample meets all parameters prescribed by the Tamil Nadu Pollution Control Board (TNPCB) for treated outlet water (Class I City Standard). Conclusion The successful test validation at Hyundai Motors India Pvt. Ltd., Sriperumbudur, reinforces the reliability and efficiency of the Nexsa Bio Sewage Treatment System. Achieving TNPCB-approved water quality standards highlights Nexsa Bio’s dedication to building a cleaner and sustainable future for industries across India. 💧 Clean water today means a sustainable tomorrow — powered by Nexsa Bio. Our Latest Blogs 26Sep admin@gmail.com Bio Septic Tanks | Uncategorized Bio Septic Tanks in India | A Revolution in Wastewater Management admin@gmail.com Uncategorized Nexsa Bio Sewage System at Hyundai Motors Meets TNPCB Water Quality Standards 18Sep admin@gmail.com Bio Septic Tank | Uncategorized RCC vs FRP Bio Septic Tanks – Which is the Right Choice for You? We Post Everything That You Need to Know Useful Links Home About Us Bio Antizyme Blog Contact Us Privacy Policies About us Our Mission, A World Powered by Renewable Energy Copyright © 2025 Nexsa Bio. All Rights Reserved.
Bio Septic Tanks in India | A Revolution in Wastewater Management

Home About Us Products STP/ETP RCC BIO DIGESTER FRP BIO DIGESTER SS TRAP BOM RO Projects & Events Blog Contact X Free Consulting How Bio Septic Tanks Are Revolutionizing Wastewater Management in India India faces a growing challenge in managing wastewater due to rapid urbanization,population growth, and industrial expansion. Traditional septic tanks often causegroundwater pollution and require frequent desludging. Here’s where bio septic tanks –especially those made of RCC and FRP – are transforming the sanitation landscape. The Problem with Conventional Septic Tanks Leakage Leakage and contamination of groundwater odor Foul odor and mosquito breeding High Maintenance High maintenance and frequent desludging How Bio Septic Tanks Work Bio septic tanks use anaerobic bacterial culture and bio-media to decompose solid waste into water and gas. The result? Treated effluent that is safe, odorless, and non-toxic. https://youtu.be/TwYOPOe98SE?si=E8ndDWiNEyVjpYZQ Why RCC & FRP Bio Septic Tanks Are Changing the Game RCC Bio Septic Tanks Provide unmatched strength for long-term installations in apartments, schools, and industries. FRP Bio Septic Tanks Lightweight, compact, and corrosion-resistant, perfect for homes and resorts. Environmental & Social Benefits Reduces Reduces groundwater pollution by safely treating and managing wastewater. Lowers public health risks Lowers public health risks by preventing contamination and disease spread. Supports Supports Swachh Bharat Abhiyan by promoting clean, sustainable sanitation. Saves Saves space and cost with long-term, efficient, low-maintenance solutions. Conclusion RCC & FRP Bio Septic Tanks – Driving India’s Sustainable Wastewater Future From urban housing projects to rural sanitation, bio septic tanks are proving to be the futureof wastewater management in India. RCC tanks ensure durability for large-scale needs,while FRP tanks bring flexibility and ease of use to smaller setups. Together, they’rerevolutionizing how India treats its wastewater. #BioSepticTanks #RCCBioTanks #FRPBioTanks #WastewaterManagement #SustainableSanitation #SwachhBharat #EcoFriendlySolutions #CleanIndia #WaterConservation #SepticTankTechnology
RCC vs FRP Bio Septic Tanks – Which is the Right Choice for You?
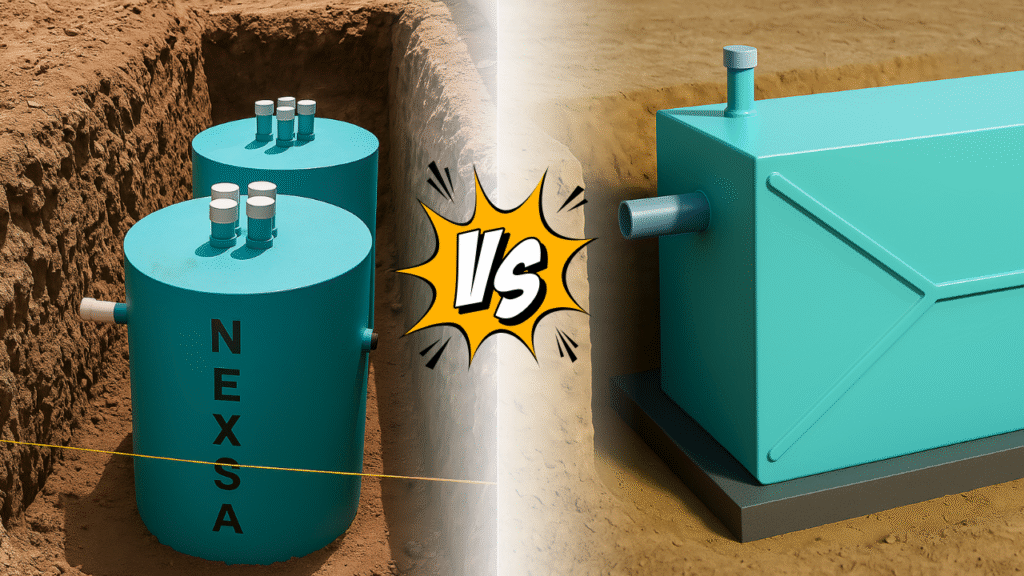
Home About Us Products STP & ETP Plants RCC Bio Septic Tank FRP Bio Septic Tank SS Bio Digester Tank SS TRAP BOM RCC Precast Water Tank Projects & Events Blog Contact X Free Consulting RCC Vs FRP Bio Septic Tanks Which is the Right Choice for You? Managing wastewater effectively is a growing necessity in today’s world. With the rise of eco-friendly technologies, bio septic tanks have emerged as a sustainable alternative to conventional septic systems. But when it comes to choosing between RCC (Reinforced Cement Concrete) and FRP (Fiber Reinforced Plastic) bio septic tanks, many homeowners, builders, and institutions face confusion. This blog will help you make an informed decision. RCC Bio Septic Tanks – Strength Meets Stability Durability Far far away, behind the word mountains, far from the countries Vokalia and Consonantia Best Suited For Large residential projects, industries, and institutions. Pros Long life (decades of usage) ,Minimal risk of leakage,Cost-effective for large installations FRP Bio Septic Tanks – Lightweight & Modern Solution Flexibility Made from fiber-reinforced plastic, FRP tanks are lightweight yet robust. Best Suited For Independent homes, villas, resorts, and space-constrained areas. Pros Easy to transport and install , Rust and corrosion resistant, Compact design with high efficiency RCC vs FRP – Quick Comparison Summary If you need a long-term, heavy-duty solution, RCC bio septic tanks are ideal. If you need quick installation, portability, and space savings, FRP bio septic tanks are the right choice. Both play an equally important role in ensuring clean, eco-friendly wastewater treatment. #RCCSepticTank #FRPSepticTank #WastewaterManagement #EcoFriendlyLiving #SustainableSanitation #NexsaBio #Septictank Contact Nexsa Bio for RCC & FRP Bio Septic Solutions. More Details!
